Total Internal Reflection












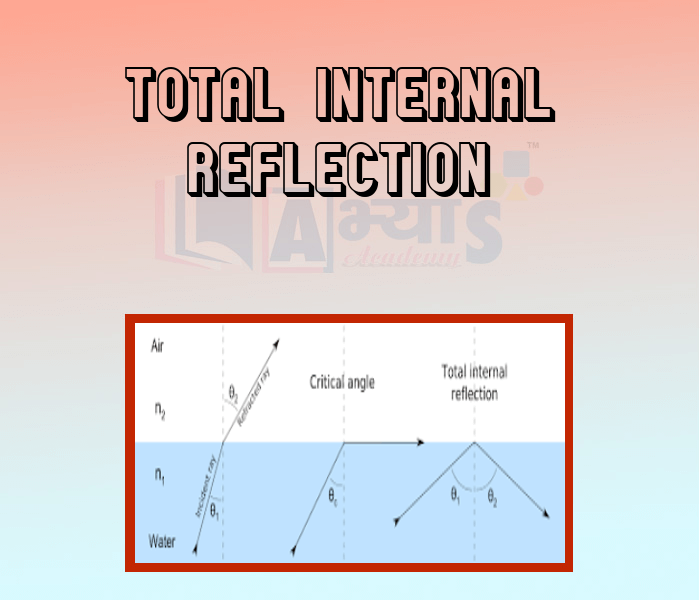
Total Internal Reflection
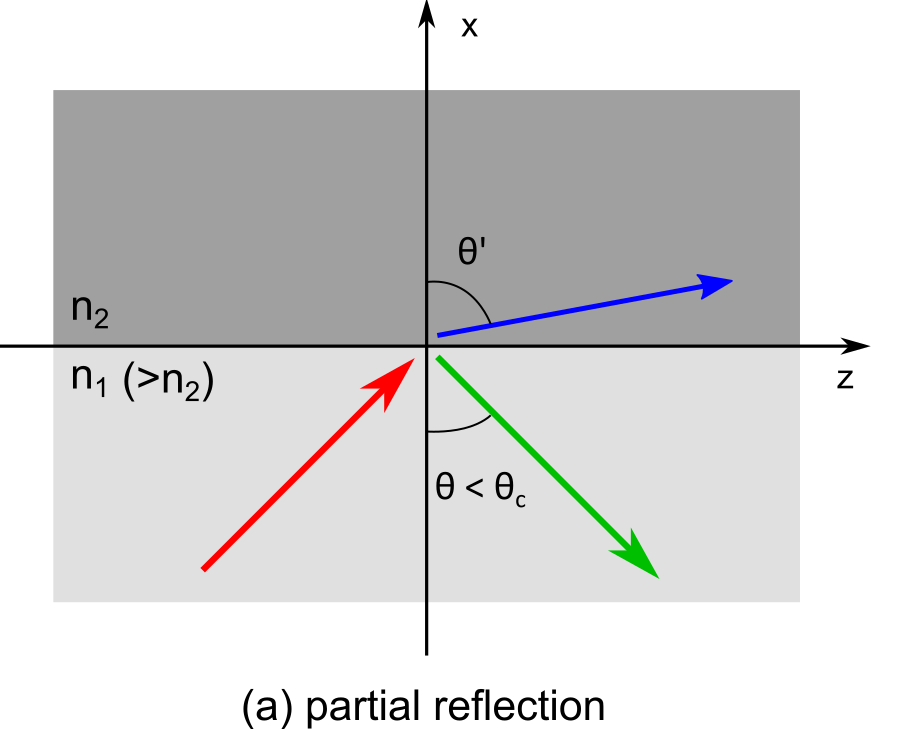
When a ray of light travels from denser(higher refractive index) to the rarer (low refractive index) medium, it bends away from the normal . This means that angle of refraction is greater than angle of incidence
. With increase in the angle of incidence, the angle of refraction also increases.The figure below shows the incident ray in red colour, the refracted ray with blue colour and the green colour ray shows the part of ray which is reflected.
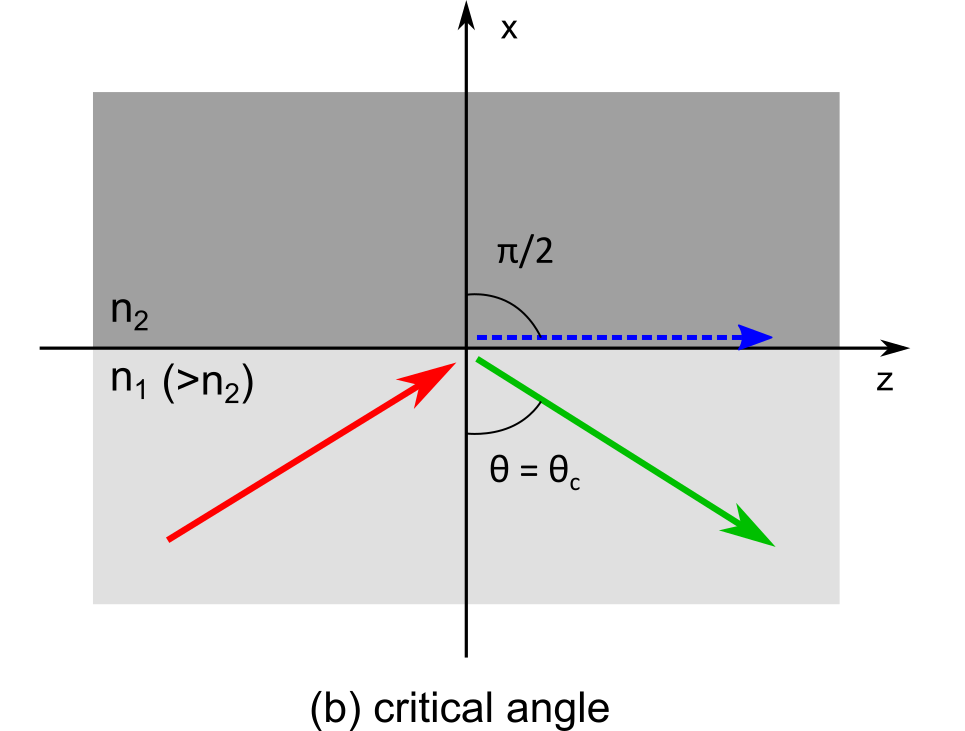
At a particular value of called as critical angle the angle of refraction becomes
.At this angle refracted ray then comes out parallel to the surface seprating the two media The figure below shows the incident ray in red colour, the refracted ray with blue colour and the green colour ray shows the part of ray which is reflected. We see that the blue ray grazes the surface seprating the two media.
The relation between the critical angle and the refractive index is
As we increase the angle above the critical angle it results in reflecting back of the ray into the same medium. This reflection obeys the law of reflection therefore angle of reflection of ray is equal to the angle of incidence
above the critical angle. The figure below shows the incident ray in red colour, As the angle of incidence is more than the critical angle there is no refracted ray hence there is no blue coloured ray and the green colour ray shows the reflected ray, which follows the laws of reflection..
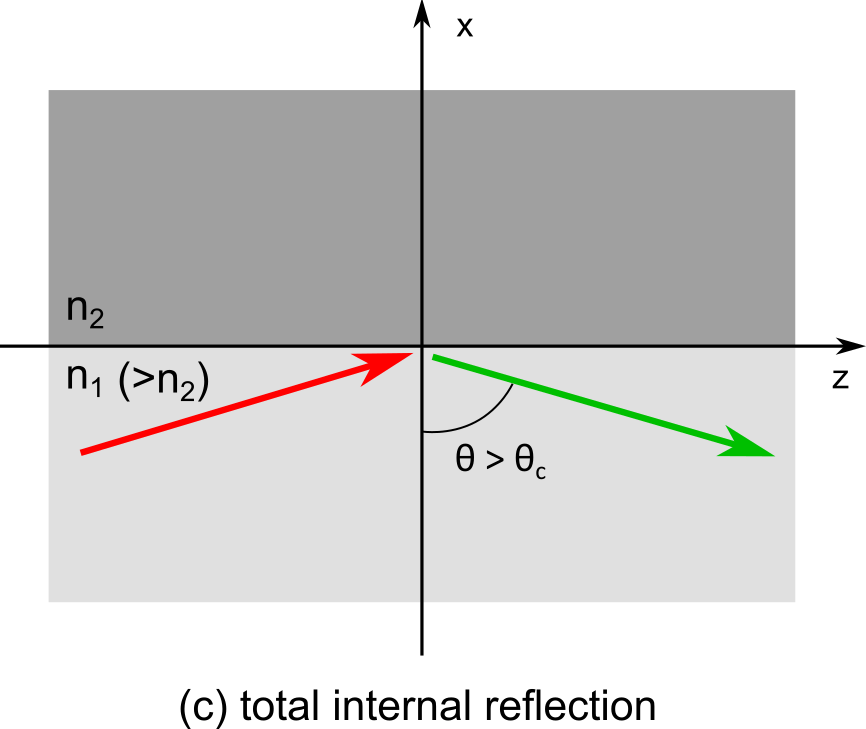
Thus the total internal reflection of light takes place when a ray of light travels in a denser medium and is incident on the boundary with rarer medium at an angle greater that the critical angle. It is known as total reflection because when a ray falls obliquely on the interface of the two transparent medium, a part of it is reflected and a part of it is refracted. When the angle of incidence is greater than critical angle, the whole of the light ray is reflected. Hence it is called total internal reflection.
For and
, from Snell's law
Substituting the values of i and r, we get
In the case of total internal reflection the higher the refractive index of the ______________ medium, the smaller is the critical angle for the pair. | |||
| Right Option : A | |||
| View Explanation | |||
For which of the following cases will the total internal reflection of light be possible? | |||
| Right Option : C | |||
| View Explanation | |||
Which of the following are correct ? (a) When a ray of light travels from high refractive index to the low refractive index medium, it bends away from the normal. (b) Total internal reflection obeys the law of reflection therefore angle of reflection of ray is equal to the angle of incidence above the critical angle. (c) The higher the refractive index | |||
| Right Option : D | |||
| View Explanation | |||
Students / Parents Reviews [10]
One of the best institutes to develope a child interest in studies.Provides SST and English knowledge also unlike other institutes. Teachers are co operative and friendly online tests andPPT develope practical knowledge also.

Aman Kumar Shrivastava
10thBeing a parent, I saw my daughter improvement in her studies by seeing a good result in all day to day compititive exam TMO, NSO, IEO etc and as well as studies. I have got a fruitful result from my daughter.

Prisha Gupta
8thMy experience was very good with Abhyas academy. I am studying here from 6th class and I am satisfied by its results in my life. I improved a lot here ahead of school syllabus.

Ayan Ghosh
8thAbhyas Methodology is very good. It is based on according to student and each child manages accordingly to its properly. Methodology has improved the abilities of students to shine them in future.

Manish Kumar
10thMy experience with Abhyas is very good. I have learnt many things here like vedic maths and reasoning also. Teachers here first take our doubts and then there are assignments to verify our weak points.

Shivam Rana
7thAbhyas is a complete education Institute. Here extreme care is taken by teacher with the help of regular exam. Extra classes also conducted by the institute, if the student is weak.

Om Umang
10thI have spent a wonderful time in Abhyas academy. It has made my reasoning more apt, English more stronger and Maths an interesting subject for me. It has given me a habbit of self studying

Yatharthi Sharma
10thA marvelous experience with Abhyas. I am glad to share that my ward has achieved more than enough at the Ambala ABHYAS centre. Years have passed on and more and more he has gained. May the centre flourish and develop day by day by the grace of God.

Archit Segal
7thMy experience with Abhyas academy is very good. I did not think that my every subject coming here will be so strong. The main thing is that the online tests had made me learn here more things.

Hiya Gupta
8thIt was good as the experience because as we had come here we had been improved in a such envirnment created here.Extra is taught which is beneficial for future.
